
- To quickly resolve a “Path Too Long” error, shorten the name of your file or folder. Right-click your file and choose Rename in the context menu. Alternatively, press F2 (or Fn + F2) to initiate the renaming process.
- The “Path Too Long” error appears when your file path exceeds 256 characters, the traditional character limit on Windows 11.
- You can increase the character limit to 32,767 characters by enabling long paths.
Seeing a “Path Too Long” error on your Windows 11 PC? You likely exceeded the character limit for file and folder paths on your computer. We’ll show you how to resolve it in four different methods, from basic fixes like renaming your file or folder to enabling long paths on your version of Windows.
Fix 1. Rename the File
To quickly reduce the characters of your file path and avoid the “Path Too Long” error, rename your file to a shorter one.
Press Windows + E to open File Explore.
Navigate to your folder and select the file that you want to move or edit. From the toolbar at the top, click Rename. Type your preferred file name and press Enter. Ensure that the entire file path is under 256 characters.
Alternatively, press F2 (or Fn + F2) on your keyboard to rename your files.
Windows has a maximum path length of 256 characters, including the drive letter, colon, backslashes, folder and file names, and more. This limit applies to editions before Windows 10 version 1607.
Newer editions after Windows 10 version 1607, including Windows 11, now support what we call “long paths.” These paths have a character limit of 32,767. Still, they are not enabled by default in Windows 11 and the traditional 256-character limit may apply.
Hence, shortening the file name will resolve the issue.
Fix 2. Rename the Parent Folder
If your file path still exceeds the character limit after renaming your file, shorten the parent folder’s name instead.
Open File Explorer (using Windows + E) and select the folder containing the file you want to modify. From the toolbar at the top, choose Rename. Alternatively, press F2 (or Fn + F2) on your keyboard to rename the folder.
Type a shorter name for your folder and press Enter.
Fix 3. Extract the Archive in the Root Folder of a Drive
The error may also appear when you’re trying to extract the contents of a compressed or ZIP file. Extract them to the root folder (the main folder) of your drive.
In File Explorer, find and click the compressed folder that you want to extract. From the toolbar at the top, click Extract all.
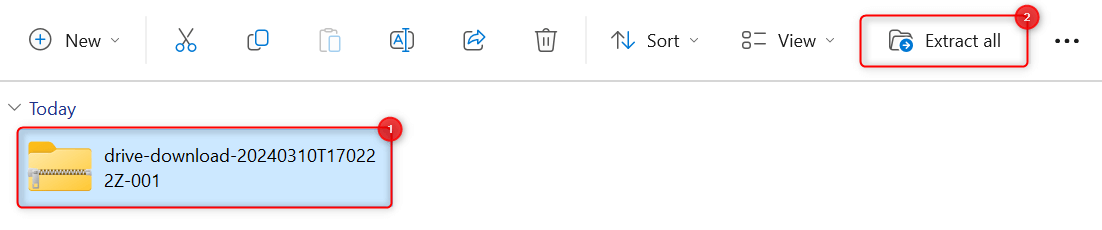
An Extract Compressed (or Zipped) Folders dialog will appear on your screen. In the Files will be extracted to this folder field, type [DRIVE LETTER]:\. For example, type C:\ or D:\ in the text box.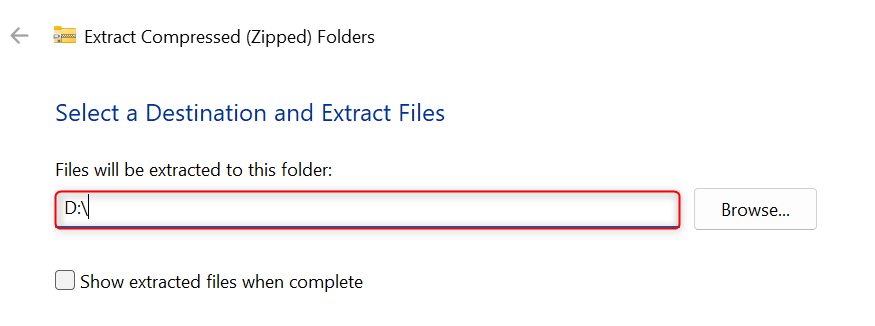
Press Enter or click Extract.
By extracting the archive in the root folder of a drive, you don’t use any subfolders and locations that can lengthen the folder path. This complies with the character limit set for your files and folders.
Fix 4. Enable Long Paths on Windows
As mentioned earlier, long paths having approximately 32,000 characters are supported but not enabled by default in Windows 11. Here’s how you enable them using the Registry Editor and the Local Group Policy Editor.
Note: Local Group Policy Editor is only available in the Windows 11 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions.
Way 1. Using Registry Editor
If your computer runs the Home edition of Windows 11, enable long paths via the Registry Editor.
Warning: Do not make any other changes to your system registry aside from the instructions below to avoid unwanted issues. We recommend you back up your system registry first in case of mishaps. In Registry Editor, click File > Export and save the registry file in a safe location.
Press Windows + R to launch Run. In the Open field, type regedit and press Enter.
A User Account Control dialog box will appear on your screen. Click Yes to proceed. Once Registry Editor opens, click the path field at the top, paste the following path, and press Enter:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem
In the FileSystem folder, double-click the LongPathsEnabled value.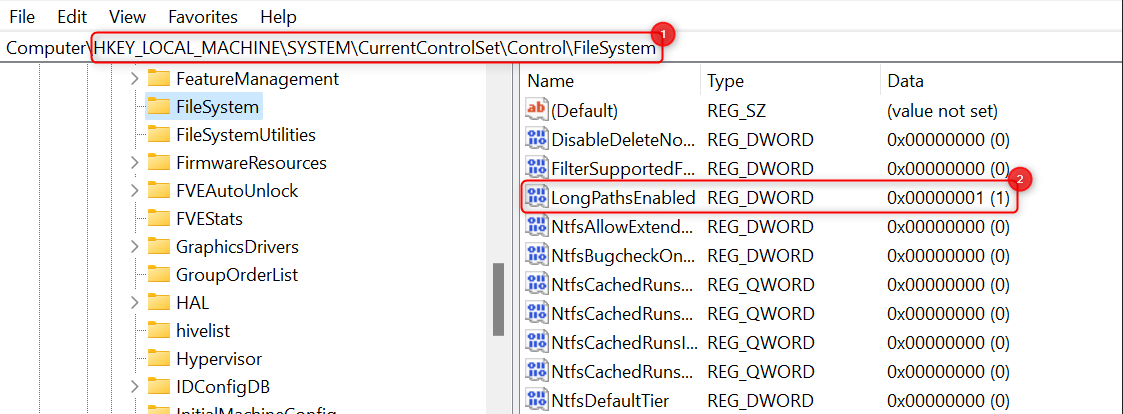
In the Edit DWORD (32-Bit) Value dialog box, click the Value data field and type 1. Click OK to save your changes.
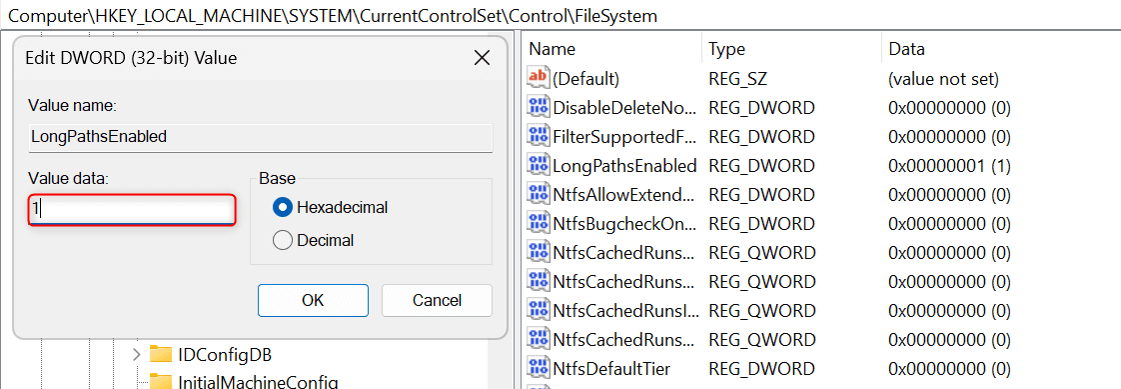
To ensure that your modifications apply, restart your PC.
Way 2. Using Local Group Policy Editor
If you have the Pro, Enterprise, or Education edition of Windows 11, use Local Group Policy Editor for an easier process. The Registry Editor method still works for these operating system versions, though.
Press Windows + R to launch Run. In the Open field, type gpedit.msc and press Enter.
This will open Local Group Policy Editor. Using the sidebar on the left, go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Filesystem. In this location, double-click Enable Win32 long paths.
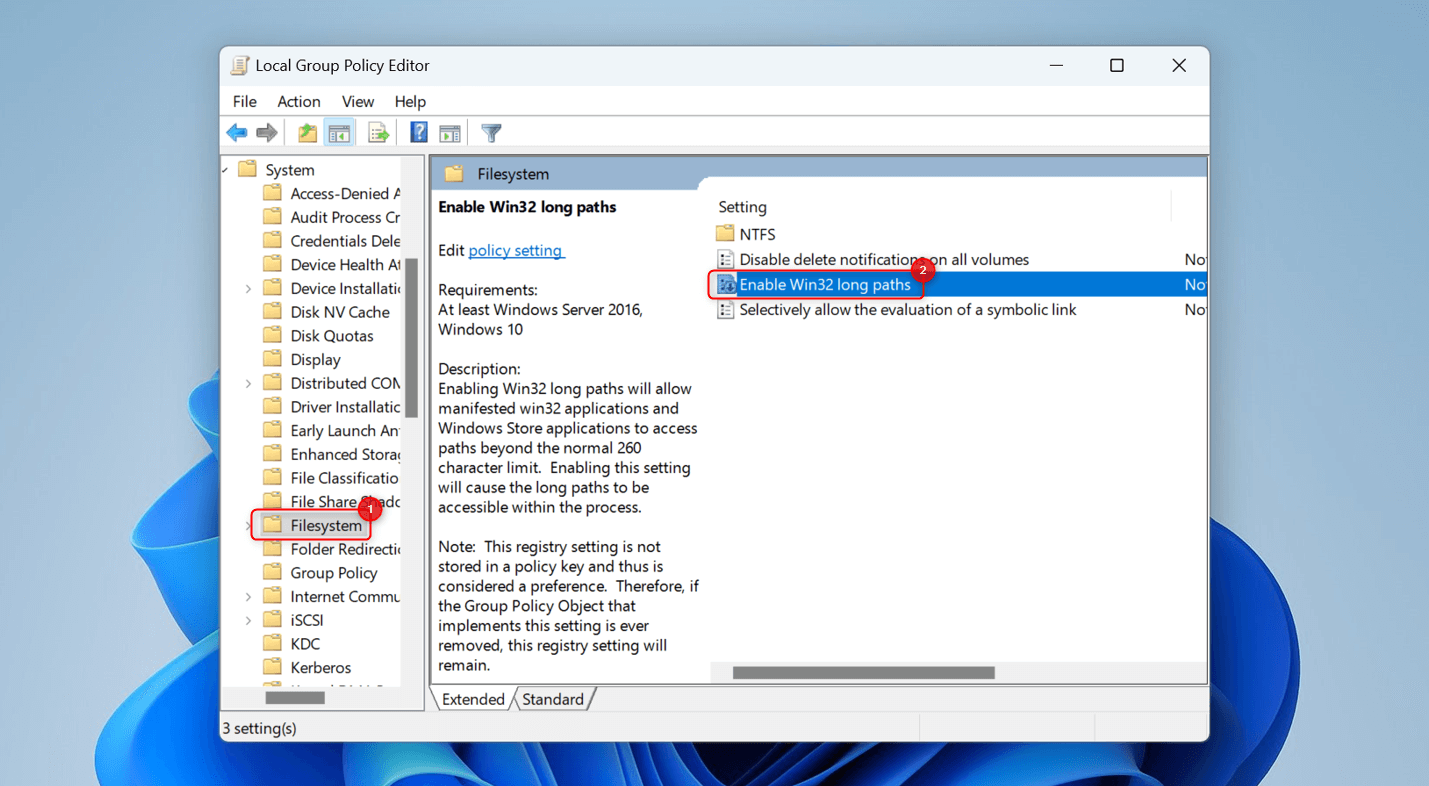
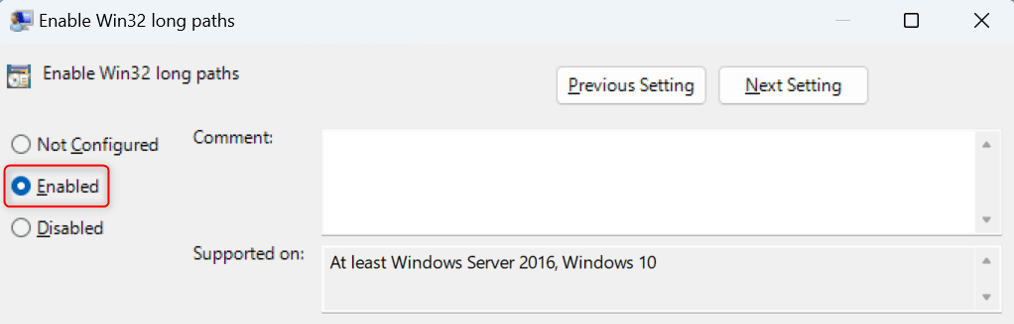
In the window that appears, choose Enabled.
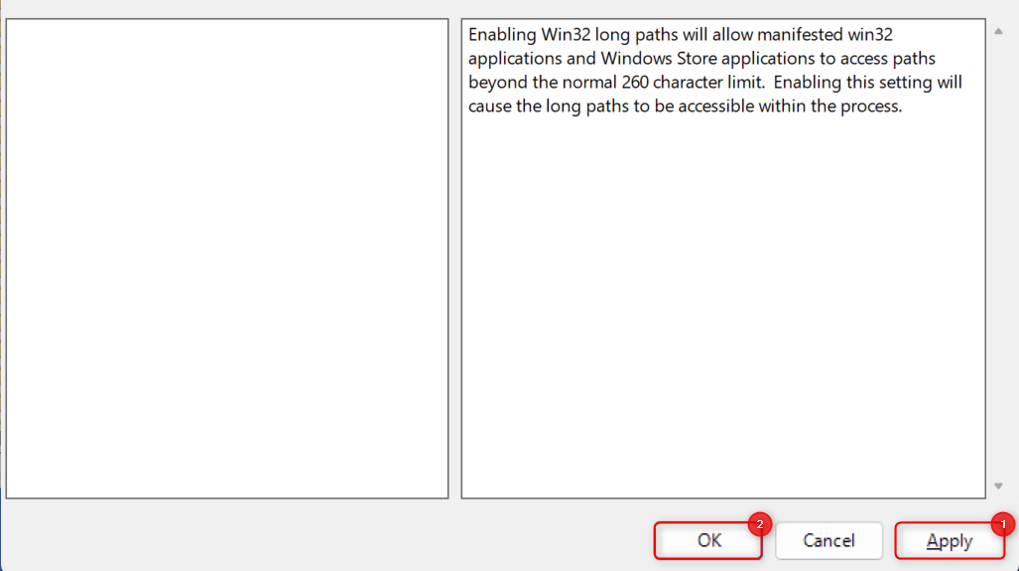
Then, click Apply > OK.
Exit Local Group Policy Editor. To apply all changes, reboot your computer.
That’s how you resolve the “Path Too Long” error on Windows 11. Now, you can move your files and folders around your storage or unarchive your compressed files. You might also want to learn how to fix an Error 0x8096002a when extracting archives on Windows 11.


